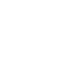
Geography
Bangladesh, a country in South Asia, covers an area of roughly 144,000 square kilometres. This area can be divided into two distinct areas – a broad deltaic plain and a small hilly region. Bangladesh is bordered on the west, north and east by land frontier with India, in the southeast with Myanmar. On the south is a highly irregular deltaic coastline of about 600 kilometres, is the Bay of Bengal. The borders of present-day Bangladesh were established during the British partition of Bengal and India in 1947, when the region became East Pakistan, as a part of Pakistan. Due to a desire for political, economic and linguistic self-determination, popular agitation and civil disobedience grew against the Pakistani state. Bangladesh gained Independence in the Bangladesh Liberation War of 1971.
Population
Economy
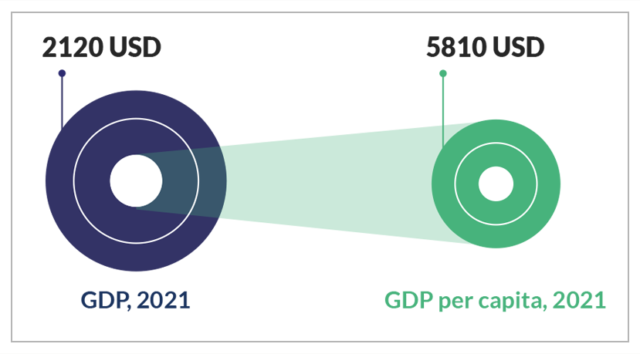
Bangladesh continues to be one of the fastest growing economies in the world, moving towards its graduation from a LDC to a middle-income country by 2024. Bangladesh’s economy expanded by a remarkable 5% in 2021 and 6.4% in 2022 (IMF). Bangladesh has a GDP of USD 357.1 billion in 2021 and GDP of USD 396.54 billion in 2022 and was ranked 41st by IMF, GDP (PPP) of USD 1000.1 billion. It has a GDP per capita income of 2360 USD and GDP (PPP) per capita of 6630 USD.
| The Spectator Index | |
| Total GDP growth in ten years (%) | |
| Countries | GDP Growth |
| Bangladesh | 188 |
| Ethiopia | 180 |
| China | 177 |
| India | 177 |
| Indonesia | 90 |
| Malaysia | 78 |
Trade
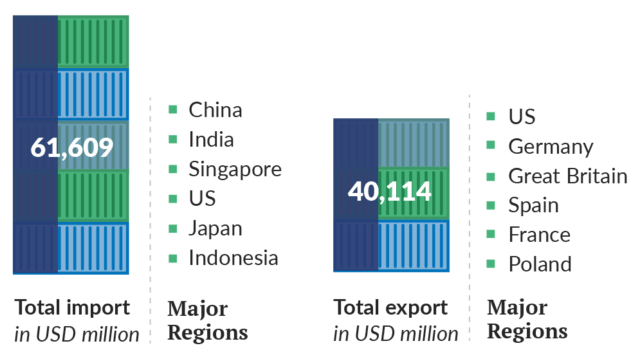
The total amount of exports was USD 40,114 million as of 2021-22(BB). The export scenario is dominated by RMG, with around 85% share (BGMEA). However, few other sectors have shown potential. Major exporting regions for RMG products were Europe (Germany, Spain, Italy, France), the US and Canada. Pharmaceutical remains promising because of the existing capacity to meet the global demand in generic drugs and TRIPS exemption, which the country will enjoy for a few more years. Bangladesh so far has exported to more than 127 countries. Bangladesh had a total import USD 61,609.1 million as of 2021-22(BB), and major commodities imported were cotton, sugar, refined petroleum, palm oil, wheat and machines. According to Bangladesh Bank, major import regions in 2021-2022 were: China (25.3%), India (16.9%), Singapore (4.8%), USA (4.4%), Japan (3.9%) and Indonesia (3.6%).
Foreign Remittance
Total remittance inflow was USD 21.03 billion as of 2021-22 and major countries were Saudi Arabia (22%), USA (16%), UAE (10%), UK (10%), Malaysia (8%), Kuwait (6%) and Oman (5%) (BB). Remittance is a major source of earnings for the country and is in 7th position globally based on amount
Infrastructure
Bangladesh has shown improvements in electrification rate and is currently providing electricity to 100% of the population (Dhaka Tribune), and produced a record high amount of electricity (12500 MW). Daily load shedding has dropped down to almost 0% between July 2019 to June 2021 (CPD). Despite high levels of improvement in access to water supply across the country, the quality of the water supplied still remains substandard. The trend, however, according to the Global Competitiveness report is towards improvement, with the score increasing from 2.9 out of 7 in 2017 to 3.1 in 2019. Bangladesh has undertaken multiple infrastructure projects to help improve the situation. Work of the Padma Bridge is being carried out as well as the metro rail, to help improve connectivity and traffic. Other ongoing projects include the Padma Rail link project, Chattogram-Cox’s Bazar Rail line, Rampal Power Project, Matarbari Coal Power Plant and Rooppur Nuclear Power plant.
Debt
Bangladesh government is committed to keeping fiscal deficit at below 5% of GDP and has so far been successful (IMF). Total central government’s debt levels were at 41.4% of GDP at 2021 and 42.5% at 2022. Bangladesh remains at low risk of debt distress with public and publicly guaranteed external debt at about 15% of GDP. External Debt stood at 12.15% of GDP. Foreign Reserve levels were kept fairly high, at USD 33 billion. Current account deficit is generally low, an average of 0.086% of GDP over the last five years. According to IMF, over the medium term, the CAD will remain broadly stable at around 2% of GDP with lower remittances to GDP, imports of capital, and imports of liquified natural gas counteracting strong export performance.
| Country | Bangladesh |
| Capital | Dhaka |
| Population | 164,689,383 (World Bank, 2020) |
| Language | Bengali. Business is mostly conducted in English |
| Currency | Taka (Sign: ৳, Code: BDT, Short Form: Tk.) |
| GDP | 324.24 billion USD (World Bank, 2020) |
| GNI Per Capita | USD 5,310 (World Bank, 2020) |
| Accounting Principles | International Financial Reporting Standards as adopted by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of Bangladesh. |